The Internet, as we all know it, is approaching a crossroads. The issues it’s currently facing are associated with the centralized model of computing (top-down, data-driven, and not necessarily human-centric), during which a finite number of private entities control the information.
In this blog, we have explained how Web 3.0 – a much better technology, will replace the Internet in the future. Instead of using something like the Internet with its centralized architecture, the world will move towards a new technology based on decentralization, trust-less & permission-less, and Ubiquitous connectivity.
- Decentralization: Decentralization shifts control (authority and responsibility) from one leading group to several smaller ones.
- Trust-less: In a Trust-less network, participants can interact publicly or privately without a trusted third party.
- Permissionless: People and companies can exchange money and goods without any authorization from a governing body.
- Ubiquitous Connectivity: Unhackable secure connection from anywhere to anywhere.
The Evolution of the Web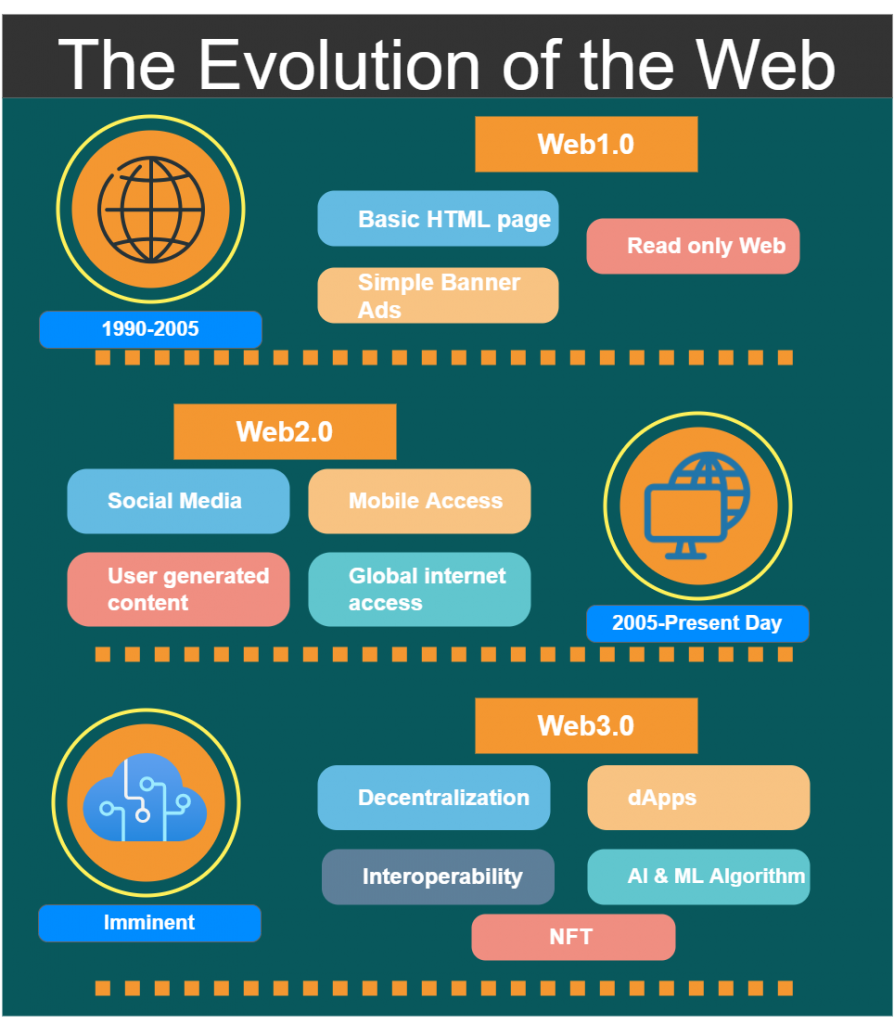
- Web 1.0 (roughly 1990-2005): Refers to the first version of the internet, and it comprised all text-based sites and the first browsers, web crawlers, and search engines that architect the net.
- Web 2.0 (roughly 2005-present day): The second version of the internet is Social Web or read-write web, which facilitates interaction between web users and sites and allows users to communicate with other users.
- Web 3.0 the “Semantic Web”(imminent): The third version is more of a vision than a structure of changes. In this version of the internet, users are creators, and information flows in more than one direction. With the power of artificial intelligence and machine learning, computers will be able to interpret and process complex information on the web.
By leveraging the power of machine learning, Blockchains, and other decentralized technologies, Web 3.0 aims to achieve open and trust-less networks where personal data is protected and people retain control over their information. Web 3.0 will also allow users to have interoperability across all systems seamlessly and enhance efficiency in many industries.
Technologies to be used for Web3.0
- Semantic Web: The goal of the Semantic Web is to make Internet data machine-readable so that is computers will be able to read and understand the content on the web.
- dApps: A decentralized application(dApps) is an application that can operate autonomously, typically through the use of smart contracts, that runs on decentralized computing and blockchain systems. Decentralized applications have been popularized by distributed ledger technologies (DLT), such as the Ethereum blockchain, on which DApps are built.
- Permissionless Blockchains: Permission-less blockchains, also known as trust-less or public blockchains, are open networks that anybody can join. There are no barriers to entry, and people are free to participate in the network’s consensus process. Since there aren’t any established authorities, the blockchain is trust-less – it allows strangers to transact with each other honestly and openly while benefiting from cryptographic accountability.
- Artificial Intelligence: Algorithms are more powerful than ever, enabling various technologies and services that can make our lives more efficient. For example, decentralized blockchain data structures now enable us to get instant access to a wealth of data that we could not rely on in the past because there was too much to keep track of. The potential applications of this technology extend far beyond targeted advertising into areas such as pharmaceutical development, climate modeling, and many more.
- AR & VR (Metaverse): AR and VR are the cornerstones for metaverse projects. Augmented reality systems depend on virtual and real environments, real-time interaction, and pinpoint accurate 3D visualizations. On the other hand, Virtual reality is an entirely simulated experience in a virtual world. It is like a daydream and feels natural and makes the user feel like they are really in the skin of their chosen character instead of themselves. The combination of AR and VR also referred to as Extended Reality (XR) that we would experience in the metaverse.
- NFTs: Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) give users the ability to own virtual objects stored on the Ethereum network. Often NFTs will serve as collectibles for users and have a monetary value attached. This means that, like art, pictures, or digital music files, people are also buying digital copies because of their rarity.
- Interoperability: Interoperability is a characteristic of a product or system to work with other products or systems, enabling different agents, services, and applications to exchange information, data, and knowledge meaningful on the web.
This matters because:
- We can send more information faster to more people, companies, and machines. You can also share information with more privacy and security.
- We can have the power to own our data and digital footprint by harnessing provable digital scarcity techniques, tokenizing it, and adding a layer of valuable information about ourselves on top.
- When investing in a new entrepreneurial project, one of the most common things a person will deal with is platform risk.
- Societies can become more profitable by cutting out the middleman and generating revenue directly from their customer base.
- An organization’s value essentially can be increased with the new peer-to-peer communication system and adjustable governance ties between participants engaged in the collaborative business environment.




