Security concerns have skyrocketed in recent times, thanks to the spurt in cyberattacks, and especially ransomware. Ransomware tactics have been known for a long time now, but it is only in recent times that it has taken on very serious proportions, propelled by the popularity of digital ‘crypto’ currencies, the Dark Net and the easy availability of ‘malware as a service’. Cyber security departments of companies are especially wary of ransomware attacks as they not only bring the business to a grinding halt, but also cause serious damage to the company’s reputation.
In order to tackle this menace effectively, it is essential to understand how ransomware works, and what is the strategy of the attackers. In this post we will try to examine these aspects.
What is ransomware?
Ransomware is a form of malware that encrypts files on an infected device and holds them hostage until the user pays a ransom to the malware operators. The payment for ransomware is most often demanded in the form of bitcoins, which is a kind of digital currency that is impossible to trace.
How does ransomware work?
The fundamental principle behind ransomware is encryption, through a mechanism called Public Key Cryptography.
Encryption is the process of hiding or obscuring the meaning of information. In the context of ransomware, it refers to the fact that ransomware codifies all the necessary files on your system, so that they appear meaningless and are rendered unusable.
When ransomware infects a system, the malware starts encrypting all the files in the system, and once it is completed, the user is presented with a threatening screen or a ransom note. The ransom note threatens the user that unless a stipulated amount is paid within specified time, the files will be rendered impossible to decrypt.
The encryption is done by a mechanism called Public Key Cryptography, also known as Asymmetric Key Cryptography. This mechanism uses advanced mathematical algorithms to code and decode the data. The unique feature of this method is that the ‘key’ used to encrypt and decrypt the files is different for encoding and decoding. This means there is always a pair of keys associated with the encryption. The public key will be used for encrypting the data, and only the matching private key can decode it.
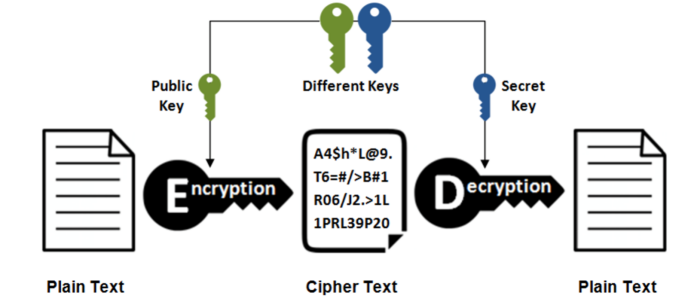
Asymmetric or Public Key Encryption
Ransomware attackers hold the private key and demand payment of a ransom for disclosing the same. If the prescribed time to pay the ransom lapses, they threaten to destroy the private key forever.
Security agencies do not recommend paying the ransom amount, as there is no guarantee that the private key will be released, and also because paying of ransom reinforces the attackers.
How does ransomware infect systems?
Ransomware typically infects systems through vulnerabilities that are yet to be patched by the system administrators. Some of the favorite channels for their entry are:
- Spam and social engineering: Where gullible internal users are tricked to click on malicious links in emails and compromised websites, which then lead to the malware being downloaded on to their systems.
- Malvertising: Again this happens due to user laxity and non-adherence to security practices. Malvertising can lead the gullible victim to follow links that lead to malware download and infection.
- Malware installation tools and botnets: These are tools that spread the malware across the network, typically within the company’s local area network.
Read: Impact of WannaCry and Petya ransomware attack
What is the strategy behind the ransomware attacks?
Ransomware attackers depend on the availability of digital currency- Bitcoin- to hide their tracks when they collect the ransom. In the past, when payment was done through bank transactions or cash, it was always possible to trace the receiver, albeit with difficulty. With Bitcoin, the receiver can remain completely anonymous and evade detection.
Another major factor aiding ransomware today is the availability of ‘malware as a service’, where inexperienced ‘script-kiddies’ armed with as-a-service malware provided by the original malware creators, become the agents or distributors for the malware, and share the ransom with the malware owners. With all the brains being provided by the malware experts, these newbies need to be armed only with criminal intent. In this way, the creators of ransomware execute the strategy of staying behind the scenes, focusing on the technical aspect of it while leaving the actual execution to newbies.
How to safeguard against ransomware attacks?
Safeguarding against ransomware depends on some simple and effective steps:
- Awareness and compliance:As we mentioned earlier in this post, humans form the weakest link in the security chain. Most of the ransomware penetration occurs due to laxity, lack of awareness, or deliberate circumvention of secure practices on the part of the inside users. Systematic education, campaigns, and constant reminders will go a long way in strengthening the human link.
- Applying security patches promptly:OS and other software vendors diligently look for vulnerabilities in their software and frequently release patches that seal these vulnerabilities. These patches must be applied immediately, so that the vulnerabilities don’t compromise the enterprise.
- Anti-malware software:There are various sophisticated tools and software now available, and these are quite effective in blocking and detecting malware activity. A set of multi-layered security tools like Seqrite’s comprehensive portfolio of the firewall, network and endpoint security tools, can prevent ransomware quite effectively.
Ransomware attacks have become more sophisticated and frequent now, and it requires eternal vigilance and care on the part of security personnel to keep it at bay. Fortunately, there are tools available now to tackle this menace. But as always, humans are the weak link in the whole chain, so a whole lot of awareness training and campaigns are needed to supplement the use of malware prevention tools.
As an IT security partner for your business, Seqrite provides comprehensive endpoint security from advanced cyber threats. To know more, visit our website or




