Zero-day vulnerabilities represent an imminent threat to cyber security, and in this case, two such vulnerabilities, CVE-2023-38831 and CVE-2023-40477, have been identified in the widely utilized WinRAR software. These vulnerabilities pose a grave concern due to their potential for remote code execution, presenting a severe threat risk.
WinRAR is a popular compression tool with half a billion users worldwide and plays an integral role in countless digital operations. This fact heightens the probable impact of these vulnerabilities, as any exploitation could severely affect the digital landscape.
These vulnerabilities require user interaction for exploitation. Remote attackers, with malicious intent, can execute arbitrary code on systems where WinRAR is installed. The software’s functionality, which includes archive creation in RAR or ZIP file formats, displays and unpacks numerous archive file formats. This further amplifies the potential for compromise as WinRAR’s ability to support the creation of encrypted archives, multi-part files, and self-extraction adds to the situation’s complexity. Furthermore, file integrity is verified using CRC32 or BLAKE2 checksum for each file within an archive, highlighting the significance of these gaps in the system.
This advisory is our detailed analysis and report of the above findings.
Why is Immediate Action Required against these Vulnerabilities?
Users using WinRAR version older than 6.23 are at risk. These vulnerabilities allow users to execute arbitrary code when attempting to view a benign file in a ZIP archive. The issue occurs when a ZIP archive may include a benign file (such as an ordinary .JPG file) and a folder with the same name as the benign file. The folder’s contents (which may include executable content) are processed while attempting to access only the benign file. This was the gap being exploited in the wild from April through August 2023 by threat actors. Breach attempts were made on online cryptocurrency trading accounts through these vulnerabilities.
CVE-2023-40477 => Recovery Volume, Improper Validation of Array Index: Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
Users who open specially crafted WinRAR archives on their devices may fall prey to the attack. The downloading of such a specially crafted archive and the opening of it on the user’s system is sufficient to allow attackers to execute arbitrary code on the device.
The issue, identified as CVE-2023-40477, is a high-severity vulnerability that exists in the processing of recovery volumes. A buffer overflow is possible when processing recovery volume names in the old RAR 3.0 format. To trigger this vulnerability, the user must start unpacking a RAR file in the same folder as a recovery archive file with a malformed name. The vulnerability exists in the processing of recovery volumes and results from a lack of proper validation of user-supplied data. This can lead to memory access beyond the end of an allocated buffer.
Software using WinRAR libraries was also affected.
The libraries unrar.dll and unrar64.dl are vulnerable. The libraries “unrar.dll” and “unrar64.dll” used by WinRAR are used in many software products (including virus scanners). If old versions of the libraries are used there, the vulnerabilities mentioned above also exist there. In the case of virus scanners, this is even more critical than with WinRAR since the anti-virus software usually runs with elevated privileges.
CVE-2023-38831 => File Extension Spoofing Vulnerability
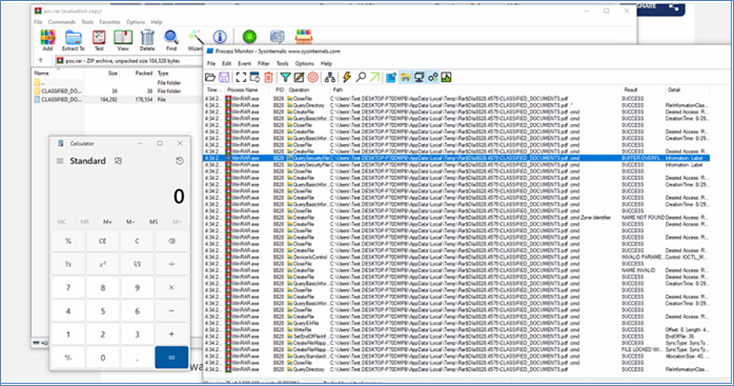
Figure 1: Opening the crafted archive results in launching calculator before the actual PDF file is opened.
On opening the archives, users cannot differentiate the harmless files hiding the malicious payload. Here, we see a pdf file and a folder with the same name.
Figure 1: Opening the crafted archive results while launching the calculator before the actual pdf file is opened.
However, when the user double-clicks on the PDF, the CVE-2023-38831 vulnerability will quietly launch a script in the folder to install malware on the device (as the calculator is launched). At the same time, these scripts will also load the decoy document so as not to arouse suspicion.
The vulnerability is triggered by creating specially crafted archives with a slightly modified structure compared to safe files, which causes WinRAR’s ShellExecute function to receive an incorrect parameter when it attempts to open the decoy file.
This results in the program skipping the harmless file and instead locating and executing a batch or CMD script, so while the user assumes they open a safe file, the program launches a different one.
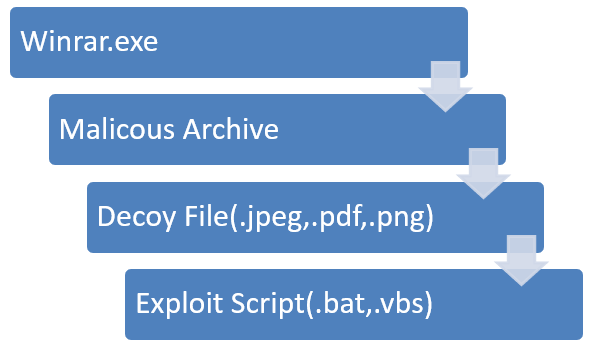
Infection Chain:
IOC:
| FileName | SHA-2 Hash |
| Trading_Strategy_2023.rar | 763df8b2db7f2f2fa0c8adb8c1cc05ff15b59e6a9756cbe9fc4a1c12329b62af |
| Cryptocurrencies2023_mpgh.net.rar | 0860e09e529fc6ccbbffebafedc27497fbbcaff57b5376fb4cc732c331d1f591 |
| Screenshot_19_04_2023.rar | 18129626041b90558607eec67616ba6d2b1ea28a280c7ba5b2bd30ebb1e2438b |
| TSG_Strategies.rar | 5a387ee6d0dcbbf2cd97379c68d8e3398d01a920873ddd45ff21dbfccb19e2ee |
| New Agreement.rar | 0059121d725a818e453e29492e78762d0a87087fcb11e484cf5ad663c1eba2bc |
Mitigation
RARLAB released WinRAR version 6.23 on August 2, 2023, and another update on August 24, 2023, effectively resolving CVE-2023-40477 and CVE-2023-38831. It is advised that WinRAR users apply this security patch with immediate effect.
Release notes: https://www.win-rar.com/singlenewsview.html?&L=0
This version also fixes another significant issue related to specially crafted archives, which helps in incorrect file initialization while extracting specially crafted archives.
Authors:
Adrip Mukherjee
Amruta Wagh




